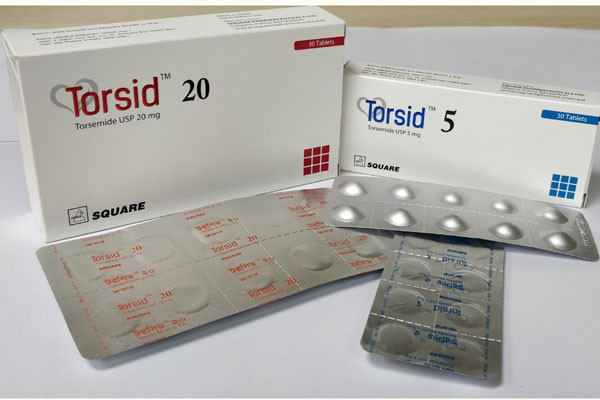

Torsid Tablet, Torasemide 20 mg
Inhouse product
-
৳11.40
৳12.00 -
৳42.75
৳45.00 -
৳16.63
৳17.50 -
৳2.14
৳2.25
Reviews & Ratings
Indications
Torsid is indicated
for the management of edema of cardiac, renal and hepatic origin.The management
of hypertension, as a sole therapeutic agent or in combination with other
classes of antihypertensive agents.
* রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Pharmacology
Torasemide inhibits
the Na+/K+/2CI- carrier system (via interference of the chloride binding
site) in the lumen of the thick ascending portion of the loop of Henle,
resulting in a decrease in reabsorption of sodium and chloride. This results in
an increase in the rate of delivery of tubular fluid and electrolytes to the
distal sites of hydrogen and potassium ion secretion, while plasma volume
contraction increases aldosterone production. The increased delivery and high
aldosterone levels promote sodium reabsorption at the distal tubules, and By
increasing the delivery of sodium to the distal renal tubule, torasemide
indirectly increases potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange
mechanism. Torasemide's effects in other segments of the nephron have not been
demonstrated. Thus torasemide increases the urinary excretion of sodium,
chloride, and water, but it does not significantly alter glomerular filtration
rate, renal plasma flow, or acid-base balance. Torasemide's effects as a
antihypertensive are due to its diuretic actions. By reducing extracellular and
plasma fluid volume, blood pressure is reduced temporarily, and cardiac output
also decreases.
Dosage & Administration
Congestive heart
failure: The usual
initial oral dose is 10 mg or 20 mg once daily. If the diuretic response is
inadequate, the dose should be titrated upward by approximately doubling until
the desired diuretic response is obtained. Single doses higher than 200 mg have
not been adequately studied.
Chronic renal failure: The usual initial oral dose is 20 mg once
daily. lf the diuretic response is inadequate, the dose should be titrated
upward by approximately doubling until the desired diuretic response is
obtained. Single doses higher than 200mg have not been adequately studied.
Hepatic cirrhosis: The usual initial oral dose is 5 mg or 10 mg
once daily, administered together with an aldosterone antagonist or a potassium
sparing diuretic. If the diuretic response is inadequate, the dose should be
titrated upward by approximately doubling until the desired diuretic response
is obtained. Single doses higher than 40 mg have not been adequately studied.
Chronic use of any diuretic in hepatic disease has not been studied in adequate
and well-controlled trials.
Hypertension: The usual initial oral dose is 2.5-5 mg once
daily. If the 5 mg dose does not provide adequate reduction of blood pressure
within 4 to 6 weeks, the dose may be increased to 10 mg once daily. If the
response to 10 mg is insufficient, an additional antihypertensive should be
added to the treatment regimen.
* রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Interaction
Increased risk of
severe hypokalaemia with amphotercin B, corticosteroids, carbenoxolone,
hypokalaemia-causing medications. Increased risk of lithium toxicity. Increased
potential for ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity with nephrotoxic or ototoxic
medications e.g. aminoglycosides. High dose salicylates may increase the risk
of salicylate toxicity. Increased risk of toxicity with digoxin. Reduced
diuretic effect with NSAIDs. Increased risk of hypotension with
antihypertensives.
Contraindications
Torasemide is contraindicated
in patients with known hypersensitivity to torasemide and other sulfonyl ureas.
It is also contraindicated in patients who are anuric.
Side Effects
Usually Torsid is well
tolerated. However, a few side effects like dry mouth, dizziness, tiredness,
skin rash, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, orthostatic hypotention
and muscle cramp may occur. All side effects usually are mild and transient.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy: Adequate and well controlled studies of
torasemide have not been carried out in pregnant woman. Because animal
reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, torasemide
can be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mother: lt is not known whether torasemide is
excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution
should be exercised when torasemide is administered to a nursing mother.
Precautions & Warnings
Precautions should be
taken while Torsid is administered in the conditions like diabetes, gout,
hypotension and liver failure.
Use in Special Populations
Use in children: Safety and efficacy of Torsid in children
have not been established.
Overdose Effects
There is no human
experience of overdoses of Torsid, but the signs and symptoms of overdosage can
be anticipated to be those of excessive pharmacological effect: dehydration,
hypovolemia, hypotension and hypokalemia. Treatment of overdose should consist
of fluid and electrolyte supplement.
Therapeutic Class
Loop diuretics
Storage Conditions
Store Torsid at room
temperature less than 30° C and keep in cool and dry place, away from moisture
and sunlight. Keep the medicine out of the reach of children.
Frequently Bought Products
Quinivir Tablet, Hydroxychloroquine Sulphate 200 mg
Miclo Ointment 10 gm tube, Clobetasone Butyrate 0.05%
Balovir Tablet, Baloxavir Marboxil 40 mg
Anzitor EZ Tablet, Atorvastatin + Ezetimibe 20 mg+10 mg
Happysol Nasal Drop 10 ml Drop, Sodium Chloride 0.9%
Bioprem Capsule, Biotin 1000 mcg
Product Queries (0)
Login Or Registerto submit your questions to seller
Other Questions
No none asked to seller yet
-
৳11.40
৳12.00 -
৳42.75
৳45.00 -
৳16.63
৳17.50 -
৳2.14
৳2.25









![D-Balance Injectable Solution (Oral & IM), Cholecalciferol [Vitamin D3] 200000 IU/ml](https://skpharma.com.bd/public/uploads/all/1ategq6XfQVotyvwuB6Tf9vm57cctsGzoGPFqHCu.webp)